Types of Aquifers
Scientists who study groundwater (often called “hydrologists” or “hydrogeologists”) generally distinguish between two types of aquifers:
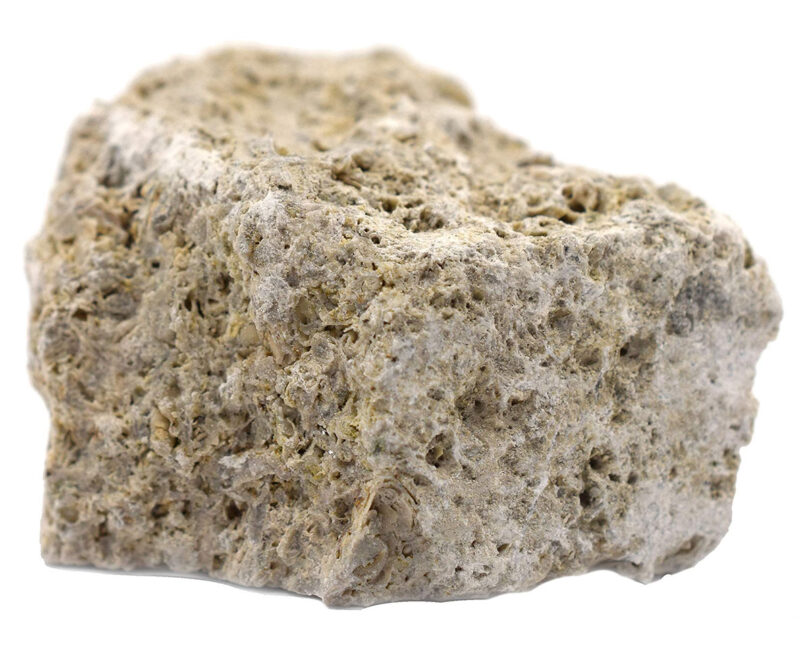
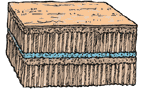
Porous Media Aquifers are made up of individual particles the size of sand or gravel up to large boulders. Groundwater moves through the openings, between the individual grains or rocks, called pore spaces.
Porous rock layers where grains are cemented to each other are called “consolidated.” Sandstones and limestones are examples of consolidated porous material.
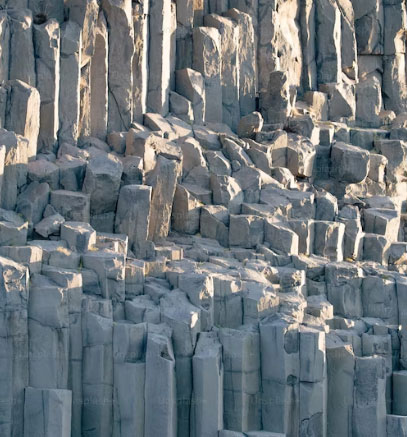
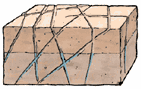
Fractured Aquifers are made up of solid rock layers where groundwater is found in fractures, joints, or cracks in the rock. Fractured aquifers are found in many different types of rocks including granite and basalt.